52 SQL DML Delete
Delete statements is used to delete rows in the tables. Delete statements should always be used together with where clause. If where clause is forgotten, then every row in the table is deleted.
Following sql will work on command line normally.
Delete from EmployeeBut dbeaver gives a warning for dangerous sql. But be aware that not every tool gives this warning. Especially, programmatic connections run every sql normally.
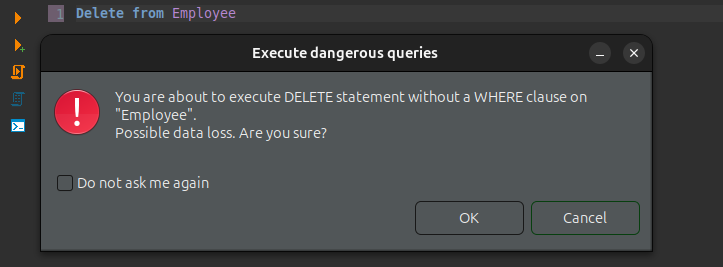
See following database specific documentation
52.1 Single row
For single row delete, we should use where PK_Column = value filter in our delete statements. Following delete statement will only delete the row with employee id 5 value.
DELETE FROM Employee
WHERE EmployeeId=5; 52.2 Multiple rows
Before deleting multiple values with update statements, we should first run the select count(*) statement to see how many rows we are deleting and this row count is consistent with our expectations.
Following sql return 3,
SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Customer
WHERE FirstName LIKE 'A%'then corresponding delete statement will delete 3 rows.
DELETE FROM Customer
WHERE FirstName LIKE 'A%';